Installation Qualification (IQ)
EU Annex 15 defines the Installation Qualification as the documented verification that the facilities, systems, and equipment, as installed and modified, comply with the approved design and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Overview
Installation Qualification (IQ) is a structured, documented verification process that confirms equipment, systems, and instruments are installed according to approved design specifications, manufacturer recommendations, and applicable regulatory requirements. It is a foundational first step in establishing a validated state and should be conducted after Design Qualification (DQ) has verified that the proposed design meets intended use, regulatory expectations, and user requirements.
Core Objectives of IQ
The primary objectives of Installation Qualification include:
- Confirm Proper Installation: Ensure the physical installation adheres to the approved design, equipment manuals, and good engineering practices.
- Verify Completeness and Conformity: Ensure that all parts, assemblies, utilities, and auxiliary systems are present and properly configured and installed.
- Establish a Documented Baseline: Establish the initial qualified state, enabling traceability, change control, and effective lifecycle validation.
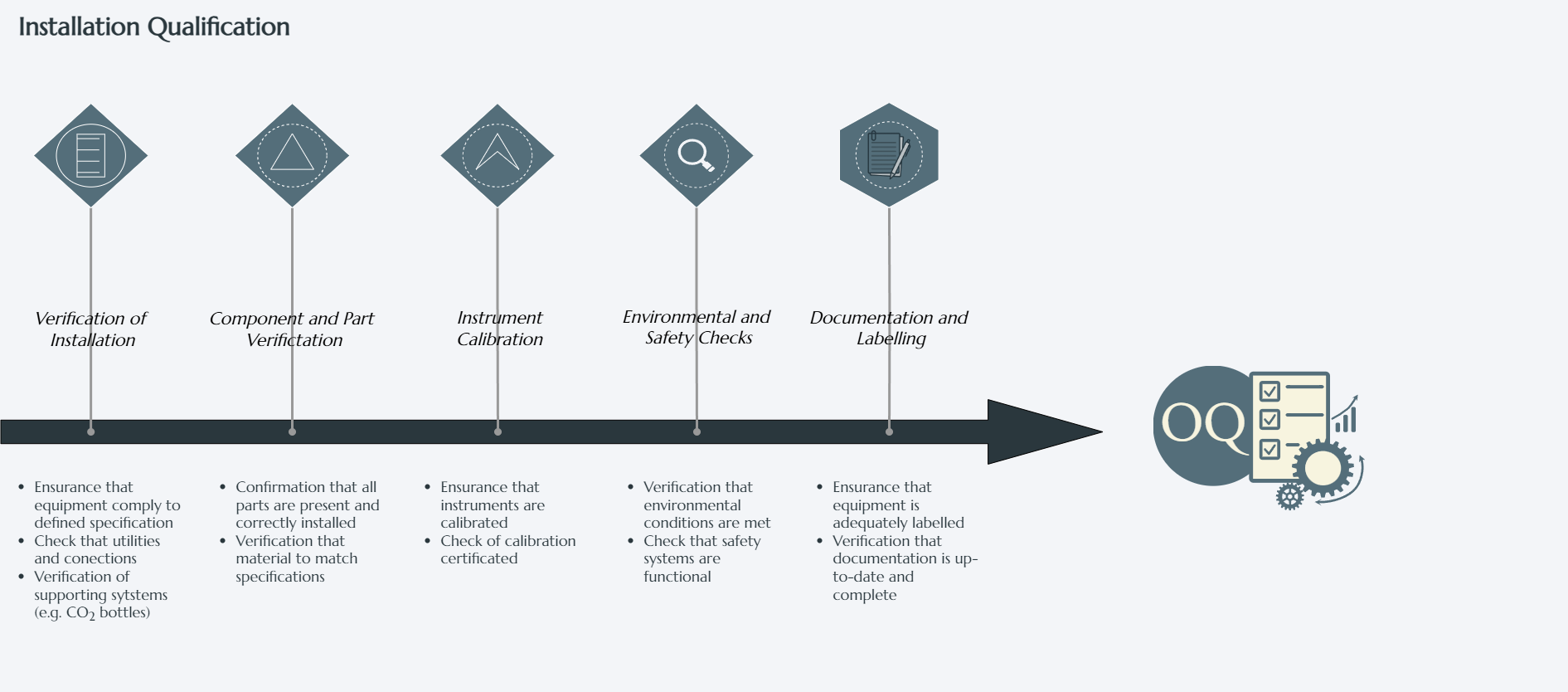
Main Activities
1. Verification of Installation
When installing equipment in regulated environments, every detail matters. Proper placement, stable construction, and reliable utilities are essential to ensure safe operations and long-term GMP compliance. The approach covers the following key aspects:
- Orientation and Location: Equipment is placed in the designated cleanroom or production area according to classified zone maps and workflow requirements.
- Structural Stability: Installations are anchored, levelled, and, where necessary, equipped with vibration control to ensure safe and reliable operation.
- Utilities and Connections: All required utilities—such as electricity, water, gases, compressed air, and data—are installed and tested for full functionality, with safety, GMP compliance, and backup systems considered where applicable.
- Installation per Drawings and Specifications: Mechanical installation follows approved piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), layout drawings, and floor plans to guarantee consistency with project design.
- GMP Compliance: Installations are designed to prevent contamination, allow effective cleaning, and ensure unobstructed access to all critical components.
2. Component and Material Verification
Thorough verification of parts and materials is essential to ensure compliance, traceability, and long-term reliability of equipment used in regulated environments. Each step safeguards product integrity and demonstrates adherence to GMP principles:
- Parts Inventory Check: All major and minor components are verified against purchase orders and supplier documentation to confirm completeness, accuracy, and traceability.
- Material Certificates: Certificates are reviewed for all materials in contact with product or critical process media, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining full documentation for audits and inspections.
- Surface Finish Checks: Stainless steel surfaces in aseptic areas are inspected to confirm required roughness values (Ra). Verification is performed through profilometry or validated vendor documentation, ensuring cleanability, aseptic design, and contamination prevention.
3. Instrument Calibration
Accurate measurement and monitoring are vital for maintaining process reliability and regulatory compliance. Calibration ensures that all critical instruments perform within defined tolerances and provide trustworthy data for regulated operations. These activities are carried out in alignment with GMP requirements (e.g., EU GMP Annex 15, ICH Q10) and international standards such as ISO 17025 for calibration laboratories:
- Instrument List Review: All instruments essential to process control, such as temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and flow meters, are identified and documented in line with qualification requirements.
- Calibration Status Verification: Each instrument’s calibration status is confirmed as current, valid, and traceable to recognized standards, ensuring accuracy and comparability.
- Calibration Labels and Certificates: Instruments are labelled with calibration date, due date, and serial number. Certificates are reviewed, approved, and archived in the IQ documentation to demonstrate compliance during audits or inspections.
- Out-of-Tolerance (OOT) Evaluation: Historical calibration data are assessed for out-of-tolerance results or recurring deviations. Corrective actions and impact assessments are documented according to GMP expectations.
4. Environmental and Safety Checks
Verifying environmental conditions and safety systems is essential to ensure both regulatory compliance and the protection of personnel. These checks demonstrate adherence to GMP principles (e.g., EU GMP Annex 1 for cleanrooms) and occupational safety standards (e.g., ISO 45001, OSHA requirements):
- Facility Conditions Verification: Ambient temperature, humidity, particle counts, and differential pressure are measured and recorded in cleanrooms or controlled zones to confirm they remain within defined specifications.
- Safety Feature Testing: Emergency stops, alarms, pressure relief valves, grounding, shielding, and interlock systems are functionally tested to confirm reliable performance in normal and emergency situations.
- Ergonomics and Accessibility: Installations are reviewed to ensure safe operator access, maintainability, and cleanability, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring compliance with both GMP and workplace safety requirements.
5. Documentation and Labelling
Clear identification and controlled documentation are critical to ensure traceability, safe operation, and long-term GMP compliance. Proper labelling and document control demonstrate readiness for audits and inspections while supporting daily operations:
- Tagging and Identification: Equipment is marked with asset tags, ID plates, and serial numbers, all of which are recorded in the equipment register and qualification documentation for full traceability.
- Labelling Verification: Flow directions, utility lines, warning signs, and cleaning status indicators (e.g., Clean/Dirty) are checked to confirm visibility, accuracy, and compliance with safety and GMP requirements.
- Document Control: All relevant documentation, such as manuals, wiring diagrams, SOPs, and maintenance logs, is verified as complete, current, and version-controlled in accordance with GMP and quality management standards (e.g., ISO 13485, ICH Q10).
IQ Documentation Requirements
Robust and well-organized documentation is critical to demonstrating a compliant Installation Qualification (IQ) process. Regulatory inspectors will expect a traceable, signed, and reviewable set of records.
1. Installation Qualification Protocol
A well-defined protocol provides the foundation for a compliant IQ. It ensures that all activities are clearly structured, reproducible, and aligned with regulatory expectations throughout the validation lifecycle:
- Scope and Objectives: Define the boundaries of the equipment or system and outline the role of IQ within the overall validation lifecycle, ensuring consistency with EU GMP Annex 15 and ICH Q10.
- Test Plan: Describe test methods, tools, responsibilities, and sampling strategy to provide a structured and transparent approach to verification.
- Acceptance Criteria: Establish clear pass/fail thresholds for each test, referencing vendor specifications or applicable standards to ensure objective, reproducible outcomes.
- Deviation Management: Specify how deviations are documented, investigated, and resolved, maintaining full traceability and integration into GMP deviation and CAPA processes.
2. Design and Technical Documentation
Comprehensive documentation ensures that design intent and technical requirements are fully captured and accessible for qualification and audits:
- Design Drawings: Approved layouts, piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), wiring diagrams, and control architecture.
- Functional Specifications: Document intended operating ranges, capacities, and critical parameters to confirm alignment with user and process requirements.
- Vendor Manuals: Maintain installation, operation, and maintenance (IOM) manuals, as well as software installation guides, in accordance with ISO 9001 and ASTM E2500.
3. Installation Checklists
Structured checklists provide documented evidence that all installation steps were completed correctly and safely:
- Mechanical Installation: Record inspections of valves, fittings, support structures, and physical alignment.
- Electrical and Control Systems: Verify power supply integrity, wiring accuracy, control functions, and safety circuits.
- Utility Verification: Confirm correct installation and performance of utilities (water, electricity, gases, compressed air), following Annex 15 and ASTM E2500.
4. Calibration Certificates
Reliable calibration is essential for accurate measurement and control. Certificates and records provide proof of traceability and regulatory compliance:
- Calibration Reports: Certificates detailing method, standard used, date, and results.
- Traceability Chain: Linkage to ISO/IEC 17025-accredited laboratories or national metrology institutes (e.g., NIST).
- Instrument Index: Central index of instruments and gauges with calibration status, history, and upcoming due dates (per EU GMP Annex 15).
5. Test and Verification Records
Accurate records demonstrate that testing was performed as planned and results are fully traceable:
- Raw Test Data: Original data sheets, logs, and electronic outputs in line with ALCOA+ principles.
- Deviation Records: Document discrepancies, assess impact, and record investigations with corrective actions (per GMP expectations).
- Cross-References: Link test records back to the executed protocol and, where relevant, to the Design Qualification (DQ).
6. Final Report
The final report consolidates the IQ process into a single, audit-ready record confirming readiness for the next validation phase:
- Comprehensive Summary: Overview of activities, results obtained, and issue resolutions.
- Protocol Traceability: Reference the executed protocol, list all completed tests, and highlight any outstanding actions.
- Approval Page: Secure signatures from Engineering, QA, Validation, and User Departments, confirming installation integrity and readiness for OQ, in compliance with EU GMP Annex 15 and 21 CFR Part 211.
Make it
Qualification with Confidence
Navigating the complex landscape of global qualification requirements—especially for Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs)—demands more than technical knowledge. It requires a strategic, risk-based approach tailored to your product, process, and facility design.
At SciReg Consult, we translate regulatory expectations into actionable qualification strategies that are practical, compliant, and scalable. Whether you're:
- Constructing a new GMP-compliant cleanroom facility for cell and gene therapies
- Qualifying high-risk, closed-system bioprocessing equipment in aseptic environments
- Aligning your process with global standards such as EU GMP Annex 15, ISO 14644, ISO 13485, and regional ATMP guidelines
We ensure your qualification lifecycle is well-documented, inspection-ready, and defensible under regulatory review.
We go beyond templated protocols. SciReg delivers:
- Integrated qualification plans: Harmonize IQ, OQ, and PQ phases with validation master plans and tech transfer timelines.
- GxP-aligned documentation: Tailored for global product submissions and inspections by EMA, FDA, and PMDA.
- Forward-compatible strategies: Supporting future scalability, data integrity, and requalification needs.